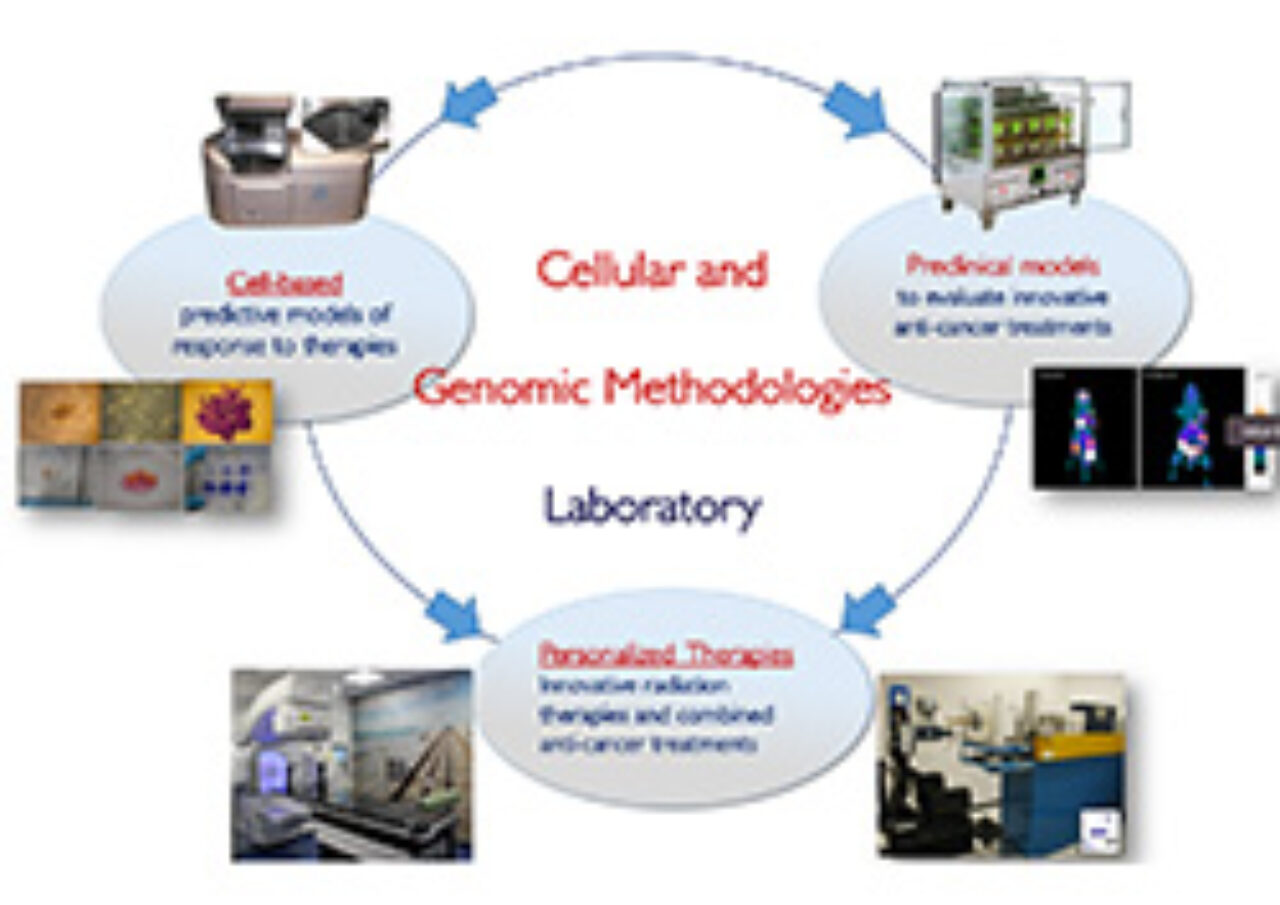
RESEARCH AREAS
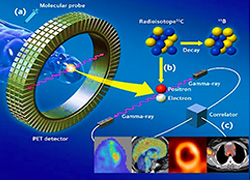
MOLECULAR IMAGING
The molecular imaging team is active in Segrate. The combination of in-vivo and ex-vivo techniques (-omics, pre-clinical rodents, clinical studies) with analysis algorithms fosters the understanding of multifactorial diseases and the selection of new biomarkers in the fields of neurology, cardiology, oncology. Methods include biostatistics, bioinformatics to integrate signals and 3D images.
- ex vivo studies : cellular transcriptomics and proteomics in animal and human specimens.
- In vivo molecular imaging (PET/SPECT/CT/MRI), pre-clinical to investigate new tracers and therapeutic targets. Clinical diagnostics to address therapeutic targets and evaluate treatment.
- Electrophysiologic imaging elettrofisiologico (MEG/EEG/ERP/high frequency neuronal recording): a)neurophysiopathology and neurophysiology of sensory networking in experimental models and humans. B) study of temporal dynamics of neural networks activation involved in cognitive functionality.
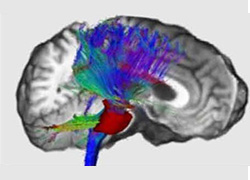
NEUROIMAGING
The neuroimaging team in Germaneto is one of the leading centres for the study of movement disorders (Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor). The research portfolio encompasses the study of other neurodegenerative disorders: multiple sclerosis, epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. Beside this activity the neurological basis of cognitive functions in normal subjects. The main scientific hypothesis is that the deep understanding of neurologic impairment is based on the knowledge of the mapping of neurophysiological pathways in normals.
The Unit is equipped with a 3T magnet with 8 and 32 channel coils(Ge; MR-750). The scientific agreement with Università “Magna Graecia” gives access to a state-of-the-art PET-MRI 3T (Siemens) and to non invasive portable equipment for functional imaging : near infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS).
Main research lines:
- Selection of new biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease and characterisation of subclinical phenotypes linked to movement disorders.
- Development of MRI acquisition protocols in structural and functional Neuroimaging and la Near Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS).
- Development of computerised diagnostic algorithms through machine learning.
RADIOTHERAPY AND BIOLOGIC EFFECTS OF RADIATIONS
The Cefalù Unit research team aims to study the biological effects of ionizing radiations, using conventional radiotherapy (electrons, X-rays and γ rays) or hadron therapy (protons and carbon ions), produced by conventional equipment (LINAC and Cyclotrons) or by innovative systems (laser driven accelerators), used alone or in combination with radiosensitizers. The main objective is the developing of innovative radiotherapy treatments for solid tumors, overcoming radio-resistance and moving towards customized treatment planning.
This radiobiological research is conducted with the integration of interdisciplinary skills, peculiar to the IBFM team of Cefalù, made up of biologists, medical physicists, IT engineers. Hence, three different contributions characterize radiobiological studies:
- A contribution in cellular and molecular biology, to describe cell survival, the biochemical and molecular pathways characterizing the response to ionizing radiations; skills in animal sciences to perform in vivo studies.
- Physical-medical contribution for the dosimetric and beam simulation aspects, useful for the irradiation set up, as well as for the results modeling;
- Computer engineering contribution for the Imaging analysis: 1) using microPET/CT images, necessary to monitor the treatments efficacy on small animals and 2) for the automatic count of cell clones on microscope images.
MOLECULAR IMAGING
NEUROIMAGING